Dental pathology is fundamental to diagnosing and managing oral diseases
1. Dental Caries (Tooth Decay)
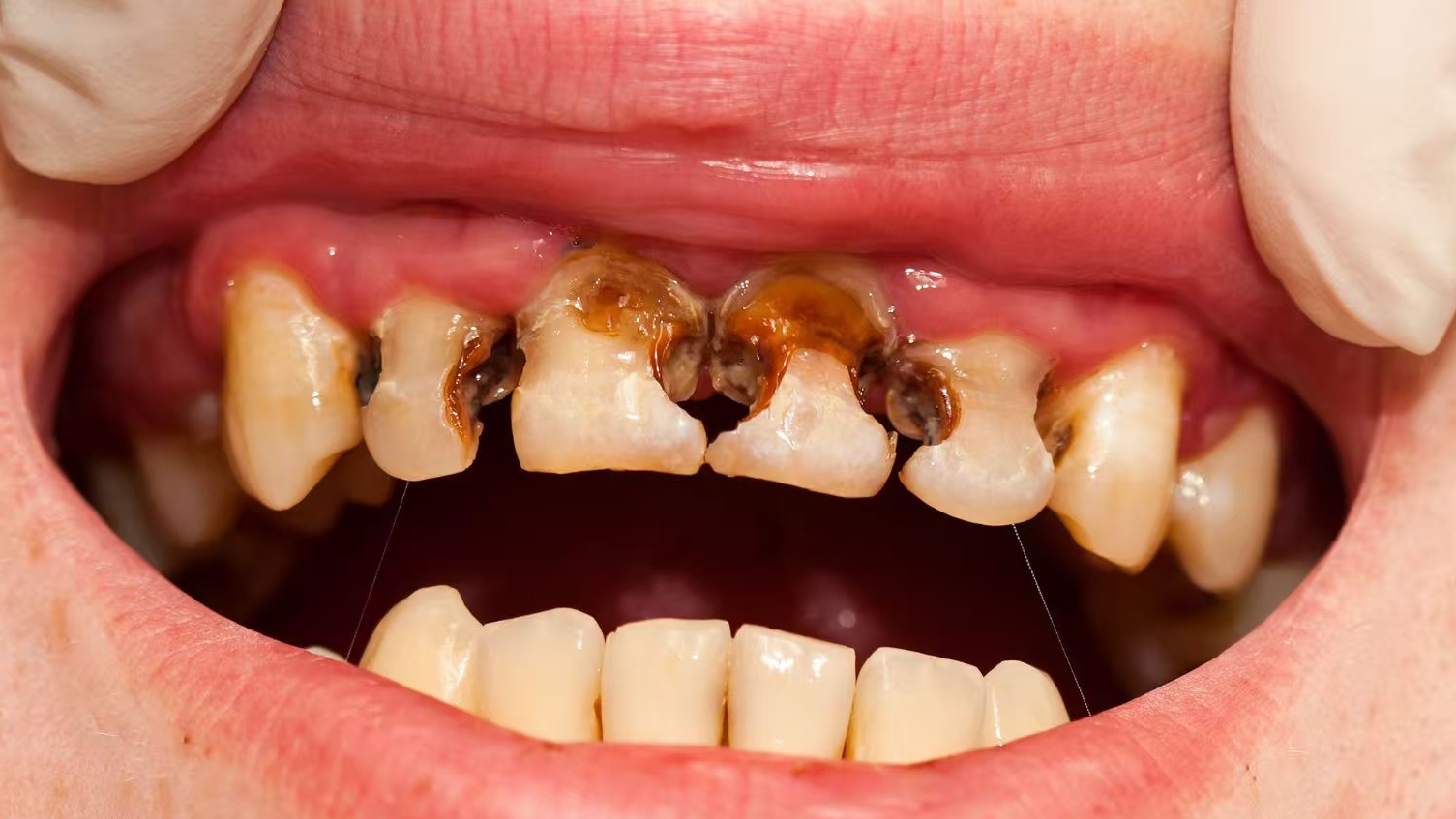
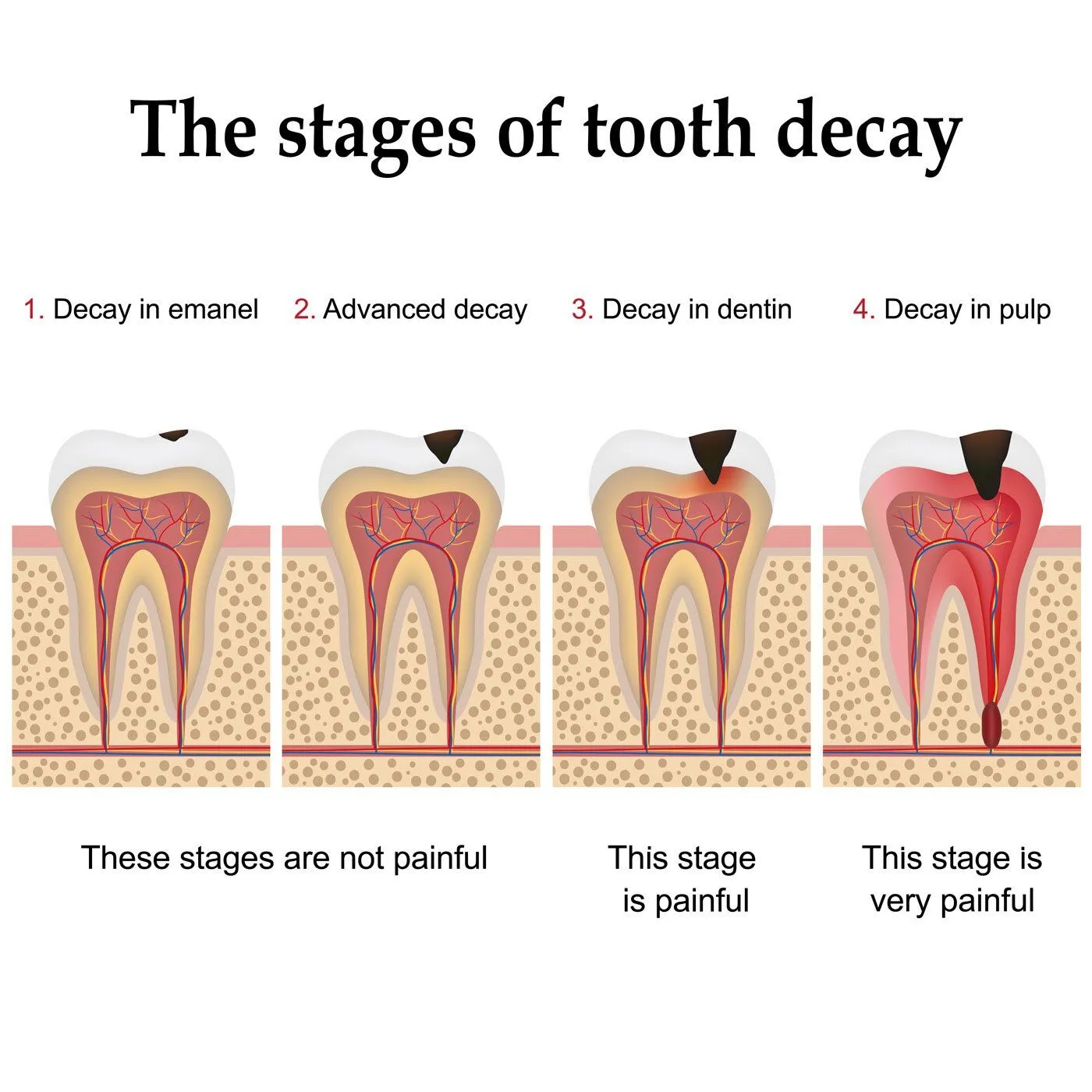
Dental caries is a microbial infection leading to demineralization of tooth structures.
- Enamel Caries (Initial Caries): Early lesion confined to the enamel, detected via radiography or visual inspection (e.g., white spot lesions).
- Dentin Caries: Progression into dentin, causing sensitivity. Classified as moderate (outer dentin) or advanced (deep dentin, risking pulp involvement).
- Pulp Exposure: Penetration into the pulp chamber, requiring endodontic intervention.
2. Pulp and Periapical Diseases
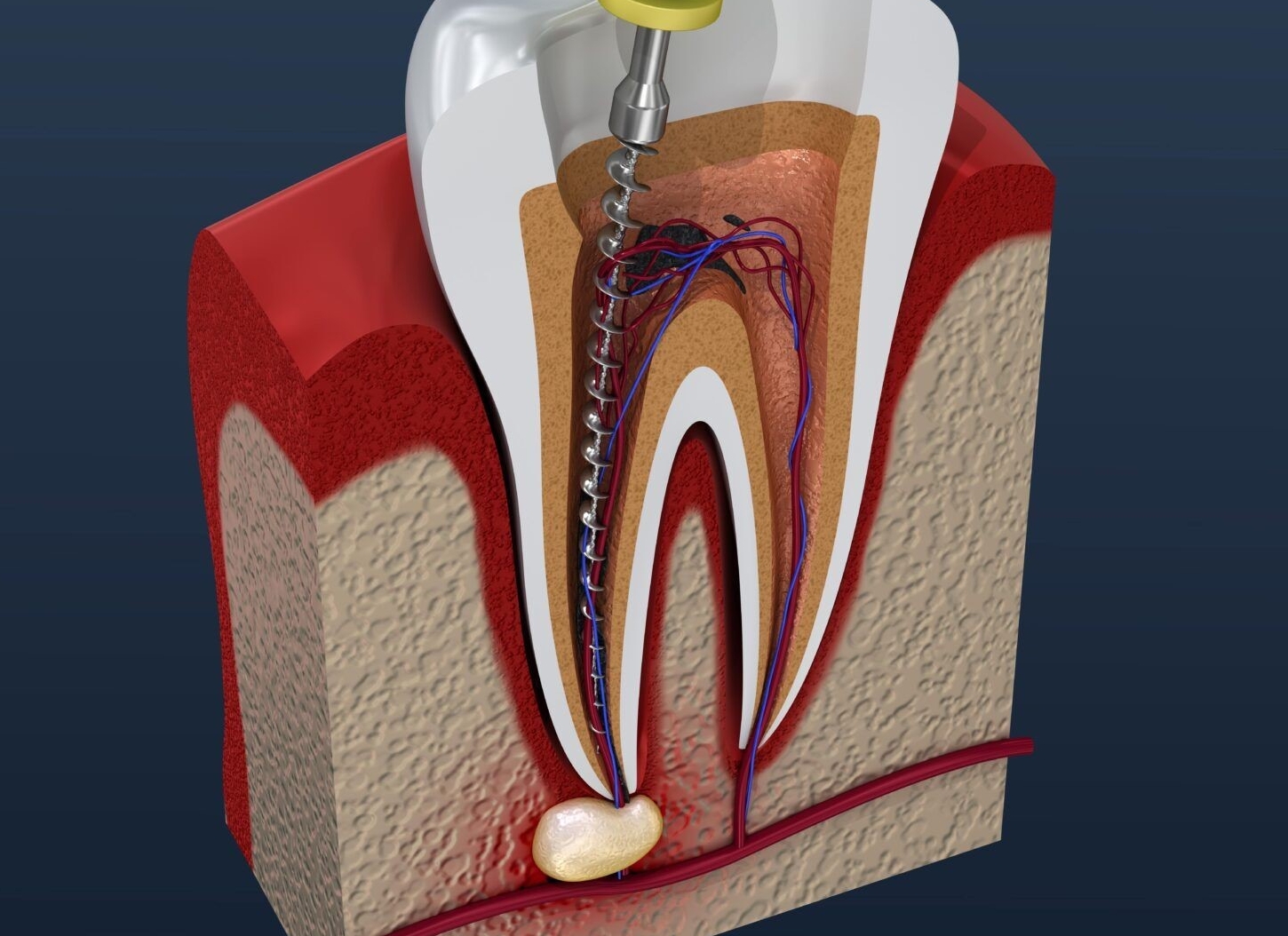
Pulpitis
Inflammation of the dental pulp, often caused by caries, trauma, or cracks:
- Acute Pulpitis: Severe spontaneous pain, thermal sensitivity, and nocturnal exacerbation.
- Chronic Pulpitis: Persistent dull pain or long-standing sensitivity, may progress to pulp necrosis.
Pulp Necrosis
Non-vital pulp tissue due to untreated infection or trauma, leading to:
- Periapical Periodontitis: Infection spreading to periapical tissues:
- Acute Periapical Abscess: Localized purulent inflammation, severe biting pain, and swelling.
- Chronic Periapical Lesions: Granuloma, cyst, or fibrous scar formation (asymptomatic until advanced).
3. Periodontal Diseases
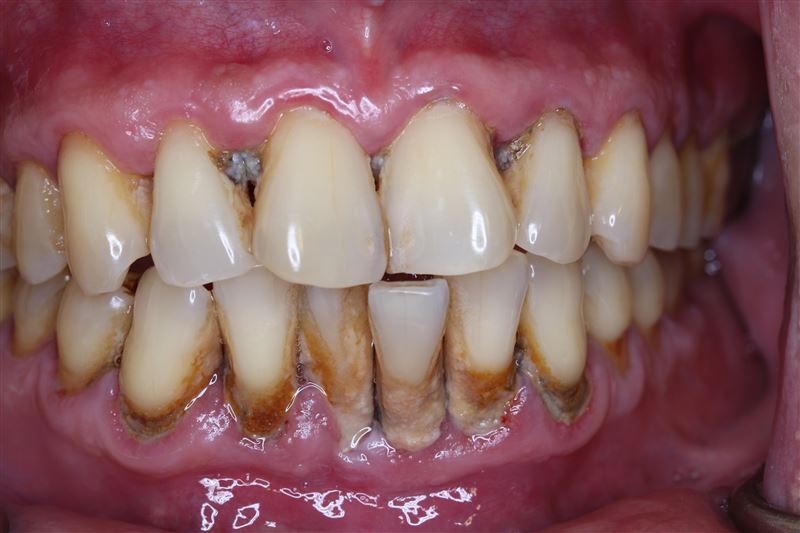
Inflammatory conditions affecting tooth-supporting tissues:
Gingivitis
Plaque-induced inflammation of gingiva:
- Marginal Gingivitis: Redness, edema, and bleeding on probing (non-destructive to alveolar bone).
- Aggressive Gingivitis: Localized (e.g., around molars/anterior teeth) or generalized, linked to poor oral hygiene.
Periodontitis
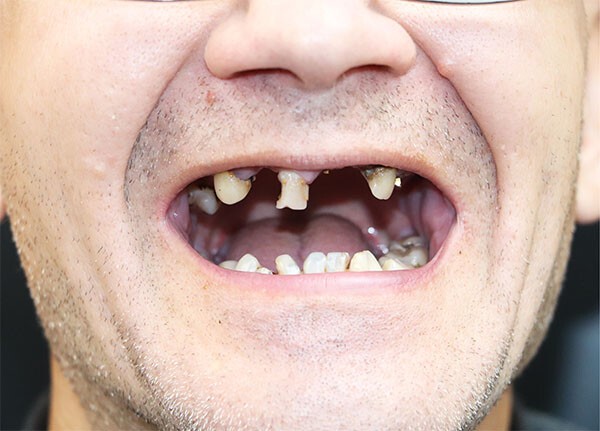
Progressive destruction of periodontal ligament and alveolar bone:
- Chronic Periodontitis: Most common form, with periodontal pocket formation (≥3mm), attachment loss, and mobility.
- Aggressive Periodontitis: Rapid bone loss, often in young patients, associated with Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans.
4. Oral Mucosal Disorders
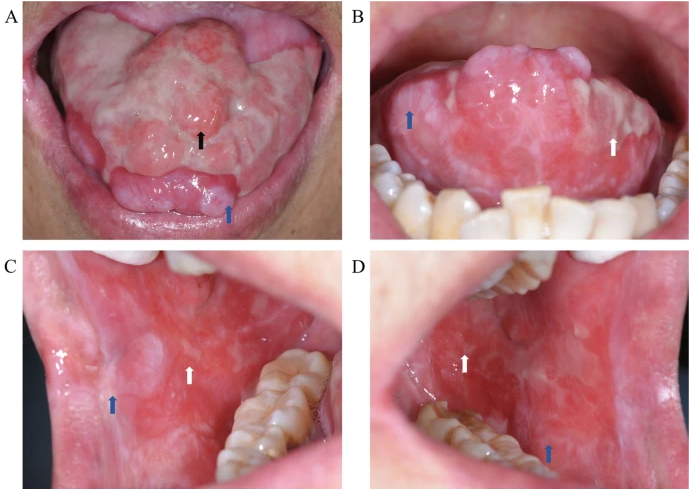
Ulcerative Lesions
- Aphthous Ulcers (Canker Sores): Painful, oval ulcers with yellow fibrin coating and red halo; minor (≤10mm), major, or herpetiform.
- Traumatic Ulcers: Caused by denture irritation, sharp teeth, or self-inflicted trauma (non-regular shape, site-specific).
Infectious Diseases
- Oral Candidiasis: Fungal infection (Candida spp.), presenting as pseudomembranous (removable white plaques), erythematous (red mucosa), or denture-related stomatitis.
- Herpetic Stomatitis: Vesicular lesions from HSV-1, common in primary infection (gingivostomatitis) or recurrent (labial/herpal lesions).
Pre-Malignant/Malignant Lesions
- Leukoplakia: White, non-scrapable plaque; 2–6% malignant potential (histology: hyperkeratosis, dysplasia).
- Erythroplakia: Red, velvety patch with higher malignant risk (often severe dysplasia/carcinoma in situ).
5. Odontogenic Tumors and Cysts
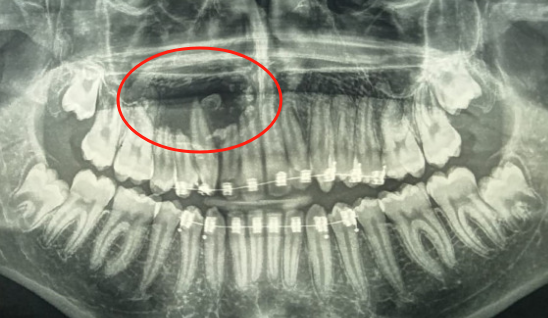
Benign Tumors
- Ameloblastoma: Locally invasive epithelial tumor (multilocular radiolucency, jaw expansion, tooth displacement).
- Odontoma: Hamartomatous growth of dental tissues:
- Compound Odontoma: Contains small, well-formed tooth-like structures (common in anterior maxilla).
- Complex Odontoma: Disorganized mass of enamel/dentin (posterior jaws).
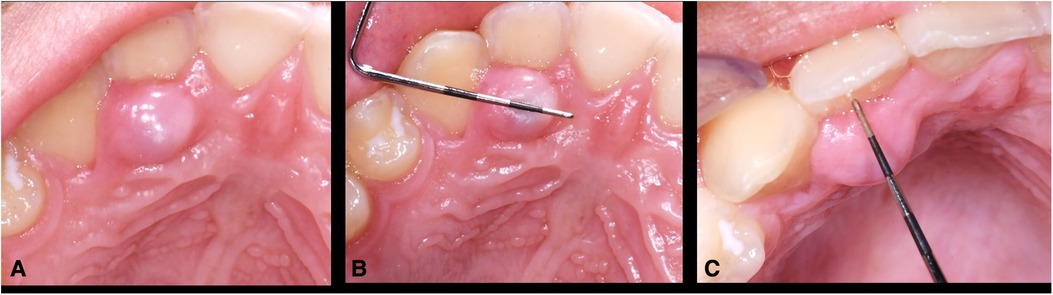
Cysts
- Radicular Cyst: Most common periapical cyst, arising from necrotic pulp (associated with non-vital tooth).
- Dentigerous Cyst: Associated with impacted teeth, enveloping crown (radiolucency around crown).