Oral health
Overview
Most oral diseases are largely preventable and can be treated at an early stage. Most cases are dental caries, periodontal disease, tooth loss and oral cancer. Other oral diseases of public health concern include stomofacial cleft, notoma (a severe gangrene that begins in the mouth and mainly affects children), and oral trauma.
Who's Global Status Report on Oral Health 2022 estimates that oral diseases affect nearly 3.5 billion people worldwide, three quarters of whom live in middle-income countries. Globally, an estimated 2 billion people have caries in permanent teeth and 514 million children have primary caries.
With urbanization and changing living conditions, the prevalence of major oral diseases continues to rise globally. This is mainly due to inadequate fluoride exposure (in water supplies and oral health products such as toothpaste), availability and affordability of high-sugar foods, and limited community access to oral health services. The sale of sugary foods and beverages, as well as tobacco and alcohol, has led to an increase in the consumption of products that contribute to oral health and other non-communicable diseases.
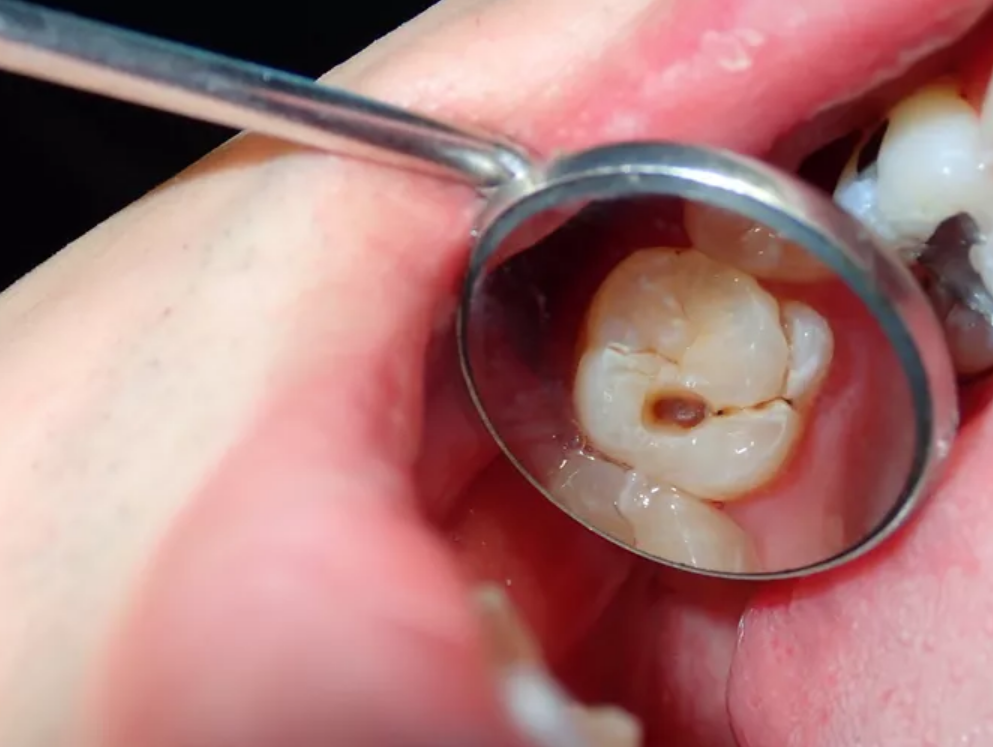
Dental caries (tooth decay)
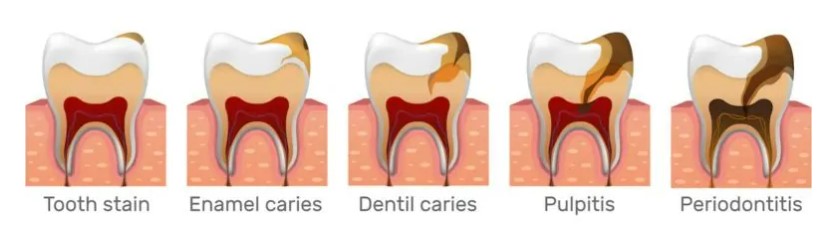
Tooth decay has appeared, if the SLATE all the way forward, the surface of the tooth forms free sugar (sugar and all food manufacturers, cooks or consumers;Plus sugar, honey, syrups and Fruchtsaften are of course foods and beverages that are converted to acid), tooth time goes by.destroy Constant intake of high amounts of free sugars, inadequate fluoride exposure and failure to remove plaque when brushing can lead to tooth decay, pain and sometimes tooth loss and infection.
Periodontal (gum) disease
Periodontal disease affects the tissues around and supporting the teeth. The disease is characterized by bleeding or swelling of the gums (gingivitis), pain, and sometimes bad breath. In heavier cases, the gums can become separated from the teeth and supporting bone, causing the teeth to become loose and sometimes fall out. Severe periodontal disease is expected to affect 19% of the world's adults, with more than 1 billion cases worldwide. The main risk factors for periodontal disease are poor oral hygiene and smoking.
Edentulism (total tooth loss)
Tooth loss is often the end point of a lifelong history of oral disease, primarily advanced dental caries and severe periodontal disease, but it can also be the result of trauma and other causes. It is estimated that the global average prevalence of complete tooth loss among people aged 20 years and older is close to 7%. In people aged 60 years and older, the global prevalence is estimated to be much higher, at 23%. Tooth loss can be psychologically traumatic, socially harmful and dysfunctional.
Oral cancer
Oral cancer, which includes cancer of the lips, other parts of the mouth and the oropharynx, is the 13th most common cancer worldwide. It is estimated that there will be 377,713 new cases of oral cancer worldwide in 2020, with 177,757 deaths. Oral cancer is more common in men and the elderly, more deadly in men than in women, and varies widely depending on socioeconomic circumstances.
Tobacco, alcohol and beetroot are the most common causes of mouth cancer. In North America and Europe, human papillomavirus infections are responsible for the increasing incidence of oral cancer in young people.
Oro-dental trauma
Oral trauma is caused by damage to the teeth, mouth, and mouth. Recent estimates suggest that 1 billion people are affected, with a prevalence of about 20% in children under 12 years of age. Oral trauma can be caused by oral factors such as misaligned teeth and environmental factors (such as unsafe playgrounds, dangerous behavior, traffic accidents, and violence). Treatment is expensive and time-consuming, and sometimes even leads to tooth loss, leading to complications in facial and psychological development as well as quality of life.
Noma
Norma is a serious disease of the oral and facial ganglia. It mainly affects children aged 2-6 who are malnourished, suffer from infectious diseases, live in extreme poverty, have poor oral hygiene or have weak immune systems.
Noma occurs mainly in sub-Saharan Africa, although it has also been reported in Latin America and Asia. Noma begins as a soft tissue injury (wound) to the gums. It then progresses to acute necrotizing gingivitis, which progresses rapidly, destroying the soft tissues and progressing further to the hard tissues and skin of the face.
According to recent estimates (since 1998), there are 140,000 new cases of Norma each year. If left untreated, Noma is fatal in 90% of cases. Survivors have severe facial deformities, difficulty speaking and eating, endure social stigma and require complex surgery and rehabilitation. If Noma is detected early, basic hygiene, antibiotics, and improved nutrition can quickly stop its progression.
Cleft lip and palate
Stomatofacial fissure is the most common craniofacial birth defect, with a global prevalence of 1 in 1000-1500 births, which varies widely across studies and populations (1). However, the mother's poor diet, smoking, alcohol abuse and obesity during pregnancy also play a role. In low-income areas, neonatal mortality is high. With proper surgery, a full recovery is possible.
Risk factors
Most oral diseases and diseases have modifiable risk factors, such as tobacco use, alcohol consumption and unhealthy diets high in free sugars, which are common to the four major NCDS (cardiovascular disease, cancer, chronic respiratory disease and diabetes).
In addition, there is a causal relationship between high sugar intake and diabetes, obesity and dental caries.
Oral health inequalities
Oral diseases disproportionately affect the poor and vulnerable in society. Research has shown a strong and consistent link between the prevalence and severity of oral disease and socioeconomic status (income, occupation, and education level). This correlation exists in population groups ranging from young children to the elderly and in high -, middle - and low-income countries.
Prevention
Through public health policies, the burden of oral diseases and other NCDS can be reduced by addressing common risk factors.
These conditions include:
Promote a balanced diet low in free sugars and high in fruits and vegetables, with water as the main beverage;
Stop using any type of tobacco, including chewing nuts;
Reducing alcohol consumption; and
The use of protective gear is encouraged during sports and when traveling on bicycles and motorcycles (to reduce the risk of facial injury).
Adequate exposure to fluoride is an important factor in preventing tooth decay.
It is recommended to use a toothbrush with fluoride toothpaste (1000-1500ppm) twice a day.
Access to oral health services
In most countries, the uneven distribution of oral health professionals and the lack of adequate health facilities to meet the needs of the population means that access to primary health services is often low. The cost of oral health care can be a major barrier to access to health services. Paying for necessary oral health care is one of the leading causes of catastrophic health care expenditures, thereby increasing the risk of poverty and economic hardship.
WHO response
The World Health Assembly adopted a resolution on oral health at the 74th World Health Assembly in 2021. The resolution recommends a shift from traditional therapeutic approaches to preventive approaches, including the promotion of oral health at home, school and the workplace, and the provision of timely, comprehensive and inclusive care within the primary health system. The resolution reaffirms that oral health should be firmly on the NCD agenda and that oral health measures should be integrated into overall health programmes.
In 2022, the World Health Assembly adopted the Global Oral Health Strategy, which envisions universal health coverage for all people and communities by 2030. A detailed action plan is being developed to help countries put the global strategy into practice. This will include a monitoring framework to track progress through measurable targets that must be achieved by 2030.